CADGME 2014
Dynamic Algebra in EpsilonWriter
This document contains the demonstrations made during the communication at CADGME 2014.
Additional lines are in blue and red. They indicate settings and actions to perform.
The demos were made with EpsilonWriter 2.401
Later versions may have a different behavior due to evolution of the software.
If you have this document as an HTML page, as it contains EpsilonWriter data, you can copy the document (Ctrl+A then Ctrl+C) and paste in EpsilonWriter to get the document with editable formulas. You can then apply the suggested actions.
Otherwise, you can get the html page at http://www.epsilonwriter.com/TMF/
You can download EpsilonWriter or use the applet at http://epsilonwriter.com
1. Equivalent drag and drop
Pedagogical dynamic algebra: only basic steps
With the tab "Calculation", choose "Dynamic Algebra: Pedagogical" and "Explain calculations on the line".
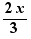
Move 2 in front of the fraction: this is a possible basic movement
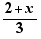
Move 2 in front of the fraction: this is not a possible basic movement
2x=3
Move 2 on 3 : this is a possible basic movement
=============================================
Calculation dynamic algebra: more powerful
With the tab "Calculation", choose "Dynamic Algebra: Strong".
Solve 2(x+2)=3
Move 2 on x+2 then 4 on 3 then 2 on -1
Factorize (x-3)(3x+2)+x(9x+6)
Move 9 in front of x and choose "Factoring HCF". Move (3x+2) in front of (x-3) . Move 3x on x
Simplify 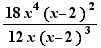
Move 18 on 12 , 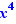 on
on 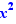 and
and 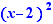 on
on 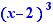
Solve 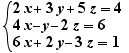
Write a 3 on the line after. Move this 3 on the = sign of the second equation, choose "Multiplication of both sides". Select the first equation and move it on the = sign of the second equation, choose "Addition side with side". Solve the second equation for z by moving 14x then the - sign. Select the second equation and move it on the = sign of the first equation, choose "Substitution". Do a Ctrl+Click on the = sign of the first equation.
2. External drag and drop
Substitution
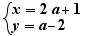
Select the above simultaneous equalities and move them on the fraction bar below. Ctrl+Click on the fraction bar.
=============================================
3. Completing the square and 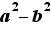
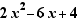
Select the expression and choose "Completing the square". Select the first 2 and move it a little to the left to factor out 2 . Select the 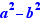 form and choose "Factorization with
form and choose "Factorization with 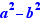 ". Ctrl+Click on the adequate - and + signs to add the numerical fractions.
". Ctrl+Click on the adequate - and + signs to add the numerical fractions.
4. Solving schemas
Solve 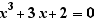
Select the equation and choose "Solve equation". You get the Cardan's formulas solving schema. Move the p= and q= on the = sign of Δ= and choose "Substitution". Use Ctrl+Click to calculate Δ. As Δ>0 , click on "ok" for the case Δ>0 and on the delete buttons for the two other cases. Select Δ=8 and move it on the = sign of 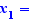 , choose "Substitution". Ctrl+Click on the inner radicals to transform
, choose "Substitution". Ctrl+Click on the inner radicals to transform 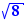 into
into 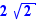 . Select q=2 and move it on the = sign of
. Select q=2 and move it on the = sign of 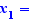 . Ctrl+Click on the two fraction bar.
. Ctrl+Click on the two fraction bar.
5. Suggestions
Solve 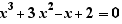
Select the equation and choose "Solve equation". Select x=y-1 and move on the = sign of the equation below, choose "Substitution". Ctrl+Click on the = sign of the obtained equation to expand and simplify. You are now in the situation 4.
6. Tables of signs and solutions of an inequality
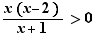
Select the inequality and choose "Table of signs filled and solution".
Select again the inequality and choose "Table of signs to fill".
7. Definition conditions of a function
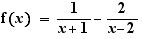
Ctrl+Click on the = sign to get the definition condition then Ctrl+Click on and to get a definition set.
8. Limits
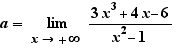
Ctrl+Click on lim to get the application of a theorem of "highest degrees". Move 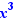 on
on  to get a simplification. Ctrl+Click on lim to get the result.
to get a simplification. Ctrl+Click on lim to get the result.
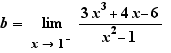
Ctrl+Click on lim to apply the substitution 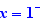 Select the numerator and choose "Numerical calculation". Select the denominator and choose "Numerical calculation". You get
Select the numerator and choose "Numerical calculation". Select the denominator and choose "Numerical calculation". You get 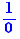 which is an indefinite expression. Delete this step by Ctrl+Z then select the denominator and choose "Calculation of a limit". You get
which is an indefinite expression. Delete this step by Ctrl+Z then select the denominator and choose "Calculation of a limit". You get 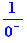 . Ctrl+Click on the fraction bar, you get the result.
. Ctrl+Click on the fraction bar, you get the result.
9. Derivatives
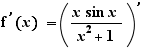
Ctrl+Click on the prime on the right of the = sign. Repeat this action until there is no prime.
10. Variation tables
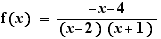
Duplicate the formula (use the "Duplicate" button or copy and paste). Put a prime on f. Select the fraction and type prime.
Ctrl+Click on the prime on the right of the = sign. Repeat this action on the prime obtained. Select the numerator and expand and simplify. Select the exponent 2 of the denominator and move it through one parenthesis on the right. Select the numerator and apply "Completing the square". Select the numerator and apply "Factorization with 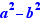 ". You get
". You get 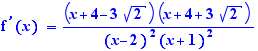 Ctrl+Click on the = sign, you get the "Variation table". Remains to fill the limits and two values of the function.
Ctrl+Click on the = sign, you get the "Variation table". Remains to fill the limits and two values of the function.
11. Several presentations of the explanations
-2x>3
Select -2 and move it over 3.
With the tab "Calculation", choose "Explain calculations in a table".
Go back to the given inequality, select -2 and move it over 3.
With the tab "Calculation", choose "Explain calculations in a table".
Select -2 and move it over 3. There is now a mathematical explanation and a gesture description.